Describe the Role of the Juxtaglomerular Complex
Identify and recognize the histological structure of the kidney and transitional epithelium in an image or microscopically. Apah-rattus pl.
Juxtaglomerular Apparatus And Juxtaglomerular Apparatus Function
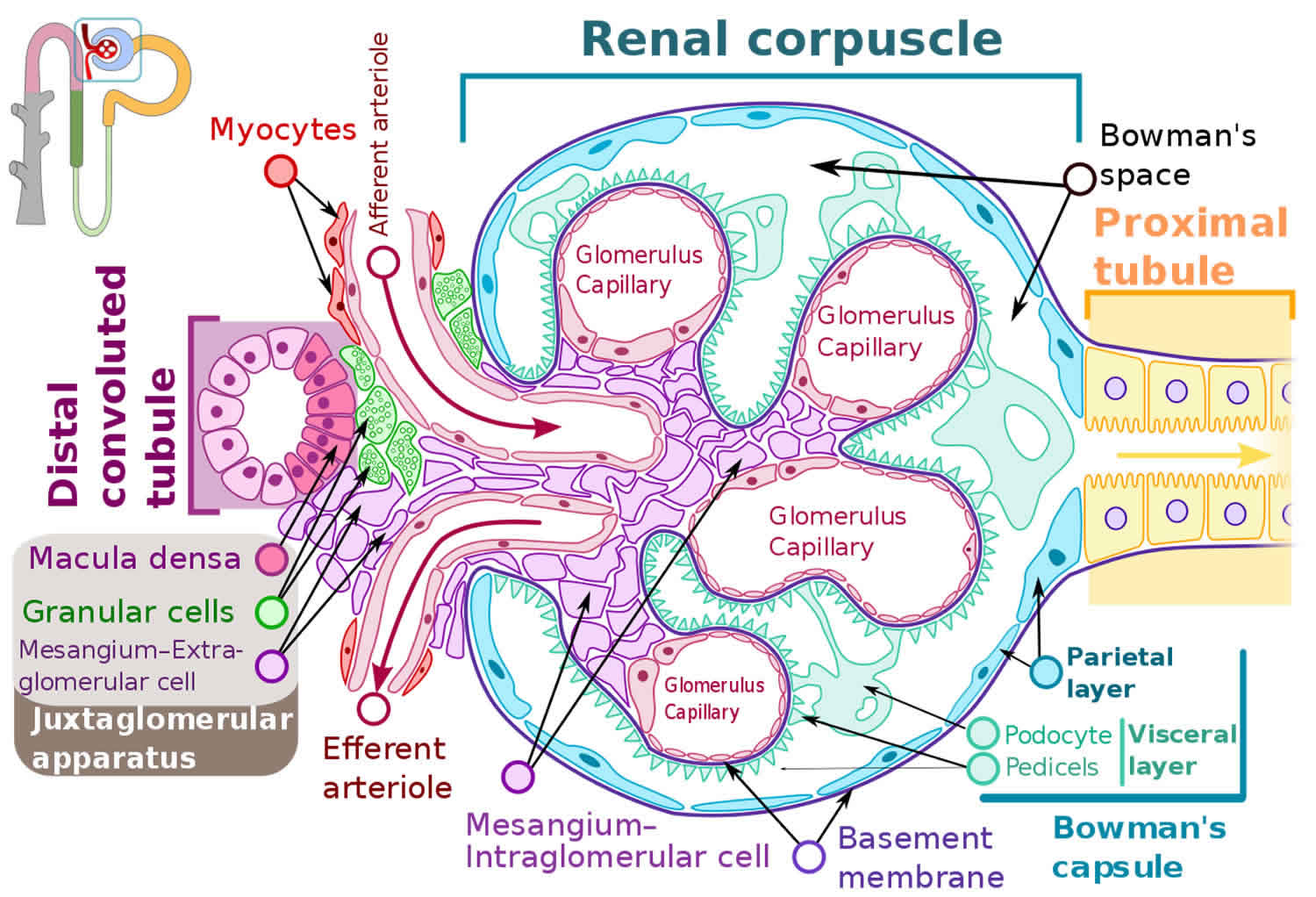
A complex consisting of a the juxtaglomerular cells which are modified smooth muscle cells in the wall of the afferent glomerular arteriole and sometimes also the efferent arteriole.

. Juxtaglomerular apparatus plays a crucial role within the renin-angiotensin mechanism. Juxtaglomerular apparatus a collective term for the juxtaglomerular cells in a nephron. The juxtaglomerular apparatus functions to maintain blood pressure and to act as a quality control mechanism to ensure proper glomerular flow rate and efficient sodium reabsorption.
How Does Juxtaglomerular Apparatus Regulate The Kidney Function. The juxtaglomerular apparatus is a specialized structure formed by the distal convoluted tubule and the glomerular afferent arteriole. Article in Russian Kovalchuk LE Melman EP.
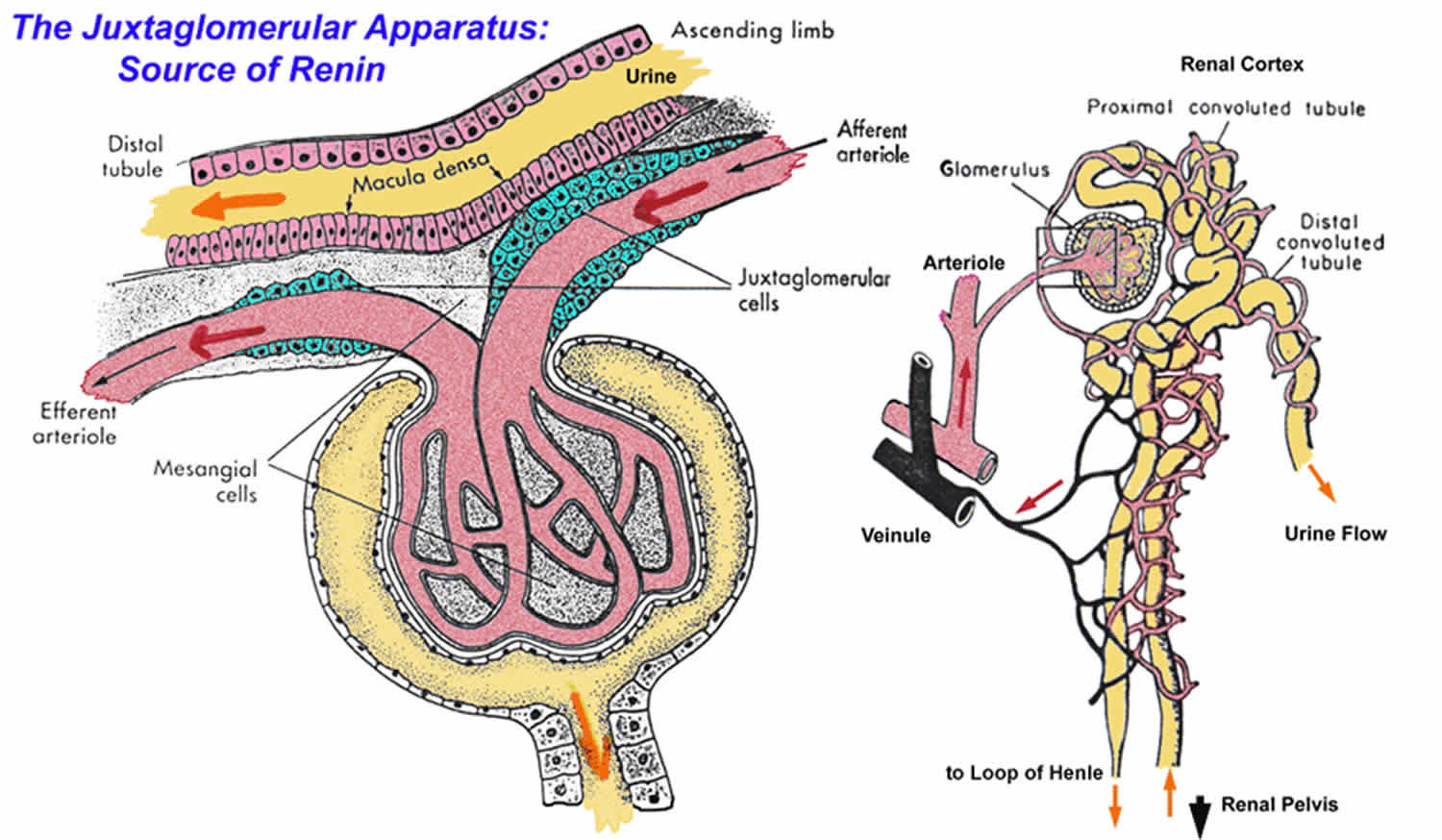
It is found between the vascular pole of the renal corpuscle and the returning DCT of the same nephron. These cells contain the enzyme renin that can sense blood pressure. They monitor the concentration of sodium and chloride ions in the filtrate of the macula densa.
Two types of contact between vascular and tubular components are observed. This structure is located near the glomerulus of the nephron the network of tangled and twisted tubes that act as a filtration system. The macula densa is a collection of specialized epithelial cells in the distal.
Juxtaglomerular cells also known as granular cells which secrete renin. When glomerular blood flow or glomerular blood pressure or glomerular filtration rate decreases it activates juxtaglomerular cells to release renin. Lacrimal apparatus see lacrimal apparatus.
The afferent arteriole in this region contains specialised secretory cells smooth muscle cells called juxtaglomerular cells that secrete renin. It is located near the vascular pole of the glomerulus and its main function is to regulate blood pressure and the filtration rate of the glomerulus. A a complex type involving distal tubule extraglomerular mesangium and proximal efferent.
The juxtaglomerular apparatus also known as the juxtaglomerular complex is a structure in the kidney that regulates the function of each nephron the functional units of the kidney. The urethra extends from the bladder to the surface of the body. Golgi apparatus see golgi apparatus.
View the full answer. The juxtaglomerular apparatus JGA consisting of an asymmetrical cuff of large granular cells in the wall of the afferent arteriole near its entry into the capsule of the nephron contains renin in the granules in the cells. Label the drawing of the nephron using the key letters of the correct terms Key a.
The juxtaglomerular apparatus consists of three types of cells. Its main function is to regulate blood pressure and the filtration rate of the glomerulus. Juxtaglomerular cells granular cells The cells of the afferent artery at the juxtaglomerular apparatus.
The juxtaglomerular apparatus located in the glomerular hilum consists of a vascular component afferent and efferent arterioles and extraglomerular mesangium and a tubular component macula densa. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. The juxtaglomerular equipment is a microscopic structure in the kidney which regulates the characteristic of every nephron.
Ascending limb of the nephron loop f. They are baroreceptors that secrete renin upon sensing a decrease in blood pressure. Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area.
B extraglomerular mesangium lacis cells which are located in the angle between the afferent and efferent glomerular arterioles. Describe the role of the juxtaglomerular complex 13. A a complex type involving distal tubule extraglomerular mesangium and proximal.
Local transmission of Tubuloglomerular Feedback TGF at its own nephron via angiotensin II AT II Systemic production of Angiotensin II AT II as part of Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System RAAS. Identify and describe the two major components of the juxtaglomerular complex and state their role in glomerular filtration. The juxtaglomerular complex has an important function in the regulation of rate of filtrate formation and blood pressure the three cell populations of the juxtaglomerular complex.
The macula densa a part of the distal convoluted tubule of the same nephron. Viewed under magnification the tiny apparatus can be seen surrounding the afferent arteriole the tube that brings fresh blood into the kidney for filtration. The juxtaglomerular apparatus helps to balance blood pressure.
Functions of Juxtaglomerlar Apparatus JGA. Describe the role of the juxtaglomerular complex. Innervation opf the juxtaglomerular complex JGC of the kidney in vertebrates.
The juxtaglomerular apparatus is part of the kidney nephron next to the glomerulus. Apparatus apparatuses an arrangement of a number of parts acting together to perform a special function. The juxtaglomerular equipment is called for its proximity to the glomerulus.
The juxtaglomerular apparatus is a specialized structure formed by the distal convoluted tubule and the glomerular afferent arteriole. The juxtaglomerular apparatus is named because it is next to the glomerulus. Glomerular capsule parietal layer e.
Two types of contact between vascular and tubular components are observed. These cells do two things. They monitor blood pressure by measuring how much the arteriole wall is stretched.
Renin is a true internal secretion of the kidney. The juxtaglomerular apparatus functions to maintain blood pressure and to act as a quality control mechanism to ensure proper glomerular flow rate and efficient sodium reabsorption. 100 1 rating Dear St.
The role of hormones in renal function. On the base of electron microscopic investigations of kidneys performed on some representatives of vertebrata fishes amphibia reptiles birds mammalia the data on their JGC innervation are presented. In this animated and interactive object learners examine the location structure and function of the juxtaglomerular JG apparatusThanks for viewing this.
The juxtaglomerular apparatus contains specialised cells of the afferent arteriole known as juxtaglomerular cells. It consists of an epithelium-lined lumen and a smooth muscle layer. Its miles discovered between the vascular pole of the renal corpuscle the returning Distal Convoluted Tubule DCT of the equal nephron.
The juxtaglomerular apparatus located in the glomerular hilum consists of a vascular component afferent and efferent arterioles and extraglomerular mesangium and a tubular component macula densa.

The Juxtaglomerular Apparatus Veterinary Histology
Juxtaglomerular Apparatus And Juxtaglomerular Apparatus Function

This Diagram Shows The Pathway Of Action Of The Renin Aldosterone Angiotensin System An Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone System Physiology Anatomy And Physiology
No comments for "Describe the Role of the Juxtaglomerular Complex"
Post a Comment